160C To Fahrenheit: Quick Conversion & Formula Guide
Ever wondered just how scorching 160 degrees Celsius truly is? The answer is a blistering 320 degrees Fahrenheit, a transformation that unlocks a deeper understanding of temperature scales and their practical applications.
Understanding temperature conversions is a fundamental skill, essential in fields ranging from scientific research to everyday cooking. While the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are the most prevalent, each with its own history and practical uses, the ability to seamlessly convert between them is paramount. This article delves into the process of converting 160 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, providing clear explanations, formulas, and helpful examples. We'll explore the origins of these scales, discuss the nuances of temperature measurement, and offer a comprehensive guide to making accurate conversions.
To grasp the significance of 160 degrees Celsius, its helpful to understand its equivalent on the Fahrenheit scale. As mentioned, 160C is equivalent to 320F. To achieve this conversion, we employ a straightforward formula. If you wish to convert 160 (one hundred sixty) degrees Celsius (°C) to degrees Fahrenheit (°F), the initial step involves multiplying 160 by 9/5 (or, you can first multiply 160 by 9 and then divide the result by 5). After performing this calculation, you must add 32 to the final result. Let's break this down further.
Here is the breakdown:
1. Multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5 (or 1.8). In our case, 160 1.8 = 288.
2. Add 32 to the result. So, 288 + 32 = 320.
Therefore, 160 degrees Celsius equals 320 degrees Fahrenheit.
This seemingly simple calculation belies the rich history and scientific principles underpinning temperature measurement. Celsius, also known as centigrade, is a temperature scale where the freezing point of water is 0 degrees and the boiling point is 100 degrees, both at a pressure of 1 atmosphere. This scale, devised by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742, is used globally for scientific work and in most countries for everyday temperature readings.
Fahrenheit, on the other hand, is primarily used in the United States. Named after German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, this scale sets the freezing point of water at 32 degrees and the boiling point at 212 degrees. The choice of these specific values has historical roots, but the scale remains an integral part of American culture.
The exact values depend on the water composition, especially the amount of salt, as well as the air pressure. Seawater, for example, contains salt and its freezing point is lower than that of pure water. This illustrates that the conversion isnt merely an abstract mathematical exercise, but a tool for understanding the world around us.
Converting 160C to Fahrenheit, or any other temperature for that matter, using a simple formula can be really easy. Let's examine the core elements of the Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion formula:
- Understanding the Formula: The general formula is: °F = (°C x 9/5) + 32, or °F = (°C x 1.8) + 32.
- Applying the Formula: Take the Celsius value (160C), multiply it by 1.8, and then add 32.
- Step-by-step:
- 160 1.8 = 288
- 288 + 32 = 320
- Result: Therefore, 160C is equivalent to 320F.
For those seeking a quick estimate, a simplified approach can be used. You can approximate the Fahrenheit temperature by multiplying the Celsius value by 2 and adding 30 to the result. For 160C:
- 160 2 = 320
- 320 + 30 = 350
This method offers a result of around 350F, which, while not exact, can be a helpful estimation.
Understanding the differences between Celsius and Fahrenheit involves considering their reference points and how they relate to the amount of heat energy. The Celsius scale bases its measurements on the freezing and boiling points of water, while the Fahrenheit scale uses different reference points. The addition of different additional values for every unit of heat energy on each scale highlights this key difference.
Due to this construction, it's impossible to say that doubling the Celsius or Fahrenheit value doubles the amount of heat energy. For example, If you want to convert 325 fahrenheit to celsius, you need to use the following formula:
- °C = (°F - 32) 5/9
- Applying the Formula: Take the Fahrenheit value (325F), subtract 32 and then multiply by 5/9 (or divide by 1.8).
- Step-by-step:
- 325 - 32 = 293
- 293 / 1.8 = 162.78
- Result: Therefore, 325F is equivalent to 162.78C.
The ability to convert between these temperature scales is important in numerous situations. Take, for example, the world of culinary arts. Many recipes, especially those from different regions, may specify oven temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. For instance, a recipe might state that you need to bake something at 160 degrees Celsius. Knowing that this equates to 320 degrees Fahrenheit ensures you can follow the instructions accurately.
This kind of conversion is useful for everything from baking to scientific experiments.
Here's a reference point in the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit, which could be helpful:
160 degrees Celsius is equal to 320 degrees Fahrenheit.
The 160 degrees Celsius value can also be converted into other temperature units,
- 160 Celsius [°C] = 433.15 Kelvin [K] 160 celsius to kelvin
- 160 celsius [°C] = 320 fahrenheit [°F] 160 celsius to fahrenheit
- 160 celsius [°C] = 779.67 rankine [°R] 160 celsius to rankine
- 160 celsius [°C] = 128 reaumur [°r] 160
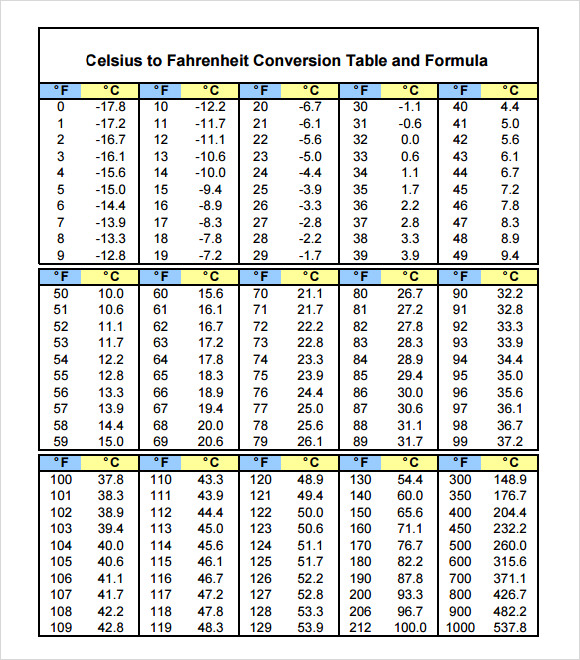
Here's an oven temperature conversion chart to find out the equivalent of celsius and fahrenheit value.
| Temperature Degrees Celsius | Degrees Fahrenheit |
|---|---|
| 160 | 320 |
| 140 | 300 |
| 160 | 325 |
| 180 | 350 |
| 190 | 375 |
| 200 | 400 |
| 220 | 425 |
This knowledge is helpful in various domains, from everyday life to scientific pursuits.
The formula and methods described above apply to convert 160 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit. The exact conversion, and indeed, the meaning of temperature itself, has implications for the understanding of our physical world.
In conclusion, understanding how to convert temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit is crucial for effectively navigating different contexts.